Introduction
Report management is found in the study conduct area under the report icon.
Report management consists of the following functions:
- Browsing attributes of existing report objects
- Updating report attributes such as report name, title, footnote, etc...
- Creating new objects with associated report attributes
- Deleting existing report objects
- Duplicating existing report objects
- Re-ordering the order number
The following shows the dialog box with all the functions as buttons and the associated
attributes for the report.
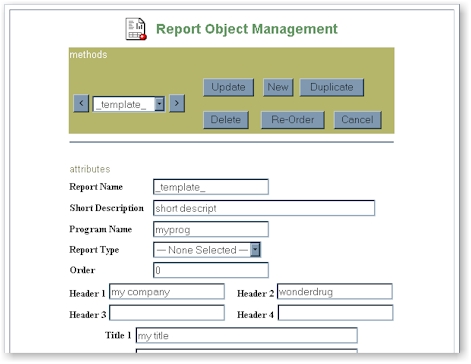
Update
This will capture all the attribute information on the current report and update
the information. Note that updating the _template_ report object will affect the
next report object created since it will use the _template_ as the starting point.
New
This creates a new report starting with attributes set by the _template_.
The following shows an example of a new report:
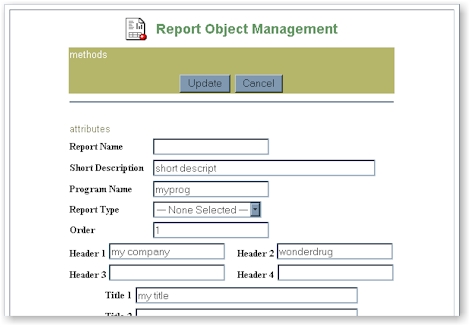
The update button will update all the attributes for this report to a new report
object. The cancel button will ignore the information entered and will not create a
new report object. Note that the order is defaulted to the next ordered value within
the report type.
Delete
This will delete the current report object that is being viewed. Note that
the _template_ is permanent and cannot be deleted.
Duplicate
This will create a new report object duplicating the attributes of the current
report. The new duplicated object contains two changed attributes including the
report name and order. The order is incremented to the next value within the
report type. The report name has the same name as the original but it has a number
attached to the end to distinguish it from the original.
Re-Ordering
This will re-order all the items found in the report object and re-assign the
order attributes with the new order numbers. The sorting order consists of the
following keys:
The report type is defined in the system configuration. Verify with the
administrator if this order is unclear. An example may be (Listings, Summary Tables,
Figures). The order numbers are re-assigned to the proper order with consecutive
integers. The following example will show how non-consecutive, non-integers are
re-numbered:
| Before |
After |
1
2.3
2.6
5
8 |
1
2
3
4
5 |
Note that decimals are allowed for order numbers for instances where new reports are
inserted in between existing entries. |